springboot mappings 注册逻辑
前面讲了怎么获取 mapping url,继续说下这些mappings 是怎么注册进去的,
来看下这个 RequestMappingHandlerMapping 的继承关系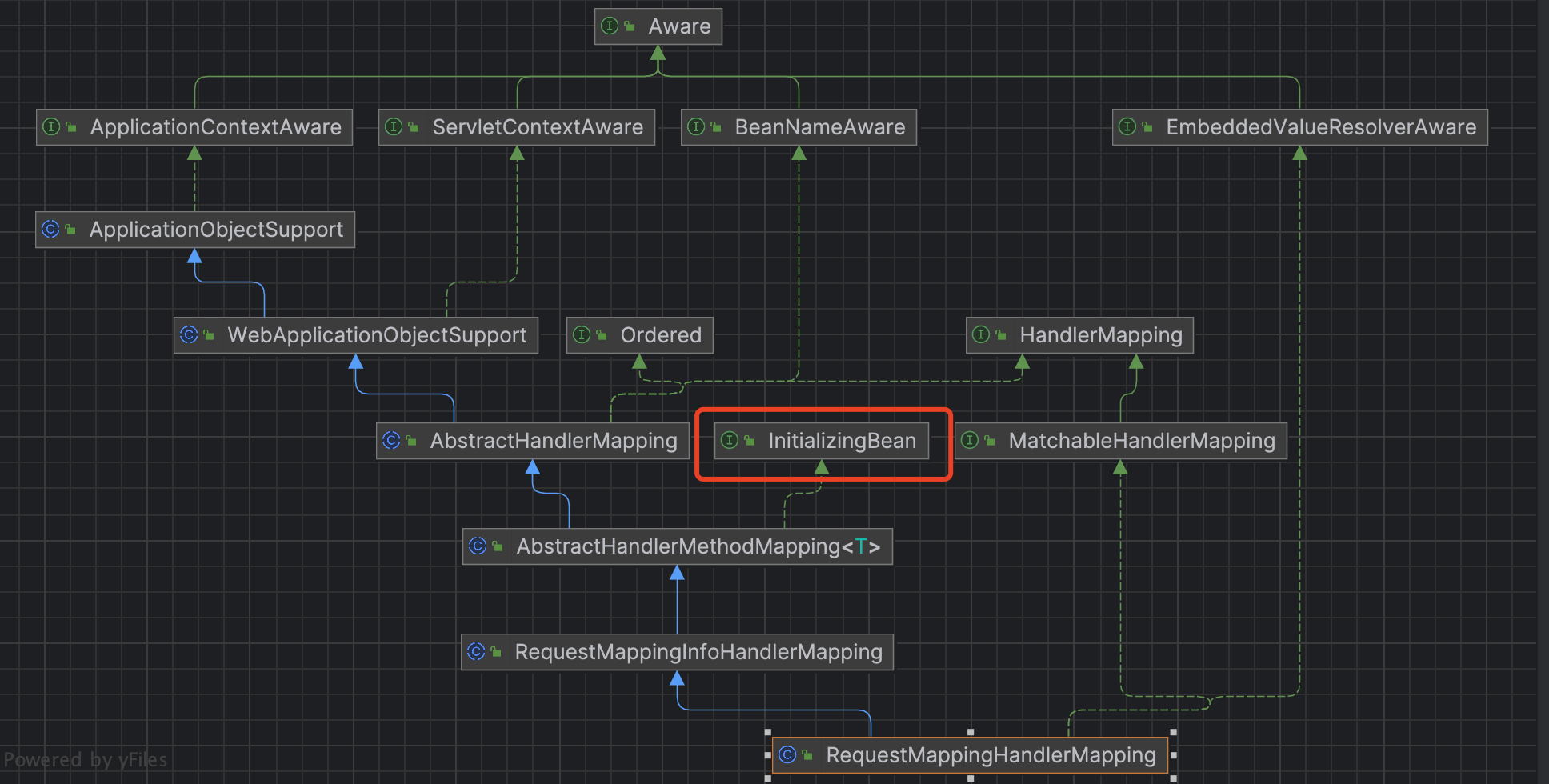
可以看到这个类实现了 org.springframework.beans.factory.InitializingBean 这个接口,然后这个 InitializingBean 提供了 org.springframework.beans.factory.InitializingBean#afterPropertiesSet 接口,可以在 bean 初始化后做一些属性设置等,
这里是调用了类本身的 afterPropertiesSet 方法和父类的1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11public void afterPropertiesSet() {
this.config = new RequestMappingInfo.BuilderConfiguration();
this.config.setUrlPathHelper(getUrlPathHelper());
this.config.setPathMatcher(getPathMatcher());
this.config.setSuffixPatternMatch(useSuffixPatternMatch());
this.config.setTrailingSlashMatch(useTrailingSlashMatch());
this.config.setRegisteredSuffixPatternMatch(useRegisteredSuffixPatternMatch());
this.config.setContentNegotiationManager(getContentNegotiationManager());
super.afterPropertiesSet();
}
父类是 org.springframework.web.servlet.handler.AbstractHandlerMethodMapping#afterPropertiesSet
具体代码很简略,就是初始化 HandlerMethod1
2
3
4
public void afterPropertiesSet() {
initHandlerMethods();
}
也就是调用了 org.springframework.web.servlet.handler.AbstractHandlerMethodMapping#initHandlerMethods1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8protected void initHandlerMethods() {
for (String beanName : getCandidateBeanNames()) {
if (!beanName.startsWith(SCOPED_TARGET_NAME_PREFIX)) {
processCandidateBean(beanName);
}
}
handlerMethodsInitialized(getHandlerMethods());
}
然后就是调用 org.springframework.web.servlet.handler.AbstractHandlerMethodMapping#processCandidateBean1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15protected void processCandidateBean(String beanName) {
Class<?> beanType = null;
try {
beanType = obtainApplicationContext().getType(beanName);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
// An unresolvable bean type, probably from a lazy bean - let's ignore it.
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Could not resolve type for bean '" + beanName + "'", ex);
}
}
if (beanType != null && isHandler(beanType)) {
detectHandlerMethods(beanName);
}
}
先是获取的 beanType,在判断 beanType 是不是 Handler,通过方法 org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.RequestMappingHandlerMapping#isHandler1
2
3
4
5
protected boolean isHandler(Class<?> beanType) {
return (AnnotatedElementUtils.hasAnnotation(beanType, Controller.class) ||
AnnotatedElementUtils.hasAnnotation(beanType, RequestMapping.class));
}
就很简单,判断是不是有 Controller 注解或者 RequestMapping 注解
然后就是判断 HandlerMethod 了,调用了 org.springframework.web.servlet.handler.AbstractHandlerMethodMapping#detectHandlerMethods1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25protected void detectHandlerMethods(Object handler) {
Class<?> handlerType = (handler instanceof String ?
obtainApplicationContext().getType((String) handler) : handler.getClass());
if (handlerType != null) {
Class<?> userType = ClassUtils.getUserClass(handlerType);
Map<Method, T> methods = MethodIntrospector.selectMethods(userType,
(MethodIntrospector.MetadataLookup<T>) method -> {
try {
return getMappingForMethod(method, userType);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Invalid mapping on handler class [" +
userType.getName() + "]: " + method, ex);
}
});
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace(formatMappings(userType, methods));
}
methods.forEach((method, mapping) -> {
Method invocableMethod = AopUtils.selectInvocableMethod(method, userType);
registerHandlerMethod(handler, invocableMethod, mapping);
});
}
}
前面先通过 getMappingForMethod 找出有 Mapping 的方法,1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
protected RequestMappingInfo getMappingForMethod(Method method, Class<?> handlerType) {
RequestMappingInfo info = createRequestMappingInfo(method);
if (info != null) {
RequestMappingInfo typeInfo = createRequestMappingInfo(handlerType);
if (typeInfo != null) {
info = typeInfo.combine(info);
}
String prefix = getPathPrefix(handlerType);
if (prefix != null) {
info = RequestMappingInfo.paths(prefix).options(this.config).build().combine(info);
}
}
return info;
}1
2
3
4
5
6
7
private RequestMappingInfo createRequestMappingInfo(AnnotatedElement element) {
RequestMapping requestMapping = AnnotatedElementUtils.findMergedAnnotation(element, RequestMapping.class);
RequestCondition<?> condition = (element instanceof Class ?
getCustomTypeCondition((Class<?>) element) : getCustomMethodCondition((Method) element));
return (requestMapping != null ? createRequestMappingInfo(requestMapping, condition) : null);
}
然后再是对 Method 循环调用 org.springframework.web.servlet.handler.AbstractHandlerMethodMapping#registerHandlerMethod
可以看到就是上一篇的 org.springframework.web.servlet.handler.AbstractHandlerMethodMapping#mappingRegistry 去存储映射信息1
2
3protected void registerHandlerMethod(Object handler, Method method, T mapping) {
this.mappingRegistry.register(mapping, handler, method);
}
最后是真的注册逻辑1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36public void register(T mapping, Object handler, Method method) {
// Assert that the handler method is not a suspending one.
if (KotlinDetector.isKotlinType(method.getDeclaringClass())) {
Class<?>[] parameterTypes = method.getParameterTypes();
if ((parameterTypes.length > 0) && "kotlin.coroutines.Continuation".equals(parameterTypes[parameterTypes.length - 1].getName())) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Unsupported suspending handler method detected: " + method);
}
}
this.readWriteLock.writeLock().lock();
try {
HandlerMethod handlerMethod = createHandlerMethod(handler, method);
validateMethodMapping(handlerMethod, mapping);
this.mappingLookup.put(mapping, handlerMethod);
List<String> directUrls = getDirectUrls(mapping);
for (String url : directUrls) {
this.urlLookup.add(url, mapping);
}
String name = null;
if (getNamingStrategy() != null) {
name = getNamingStrategy().getName(handlerMethod, mapping);
addMappingName(name, handlerMethod);
}
CorsConfiguration corsConfig = initCorsConfiguration(handler, method, mapping);
if (corsConfig != null) {
this.corsLookup.put(handlerMethod, corsConfig);
}
this.registry.put(mapping, new MappingRegistration<>(mapping, handlerMethod, directUrls, name));
}
finally {
this.readWriteLock.writeLock().unlock();
}
}
底层的存储就是上一篇说的 mappingLookup 来存储信息