我们在使用mysql的索引的时候一般会使用explain来查看执行计划,用来分析索引使用情况等1 2 3 4 SET optimizer_trace= 'enabled=on' ;SET optimizer_trace_limit= 10 ;set optimizer_trace_offset= -10 ;set end_markers_in_json= on ;
我们可以用这几个命令来开启do 1+1;1 SELECT query,trace FROM information_schema.OPTIMIZER_TRACE;
就可以看到优化器的trace1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 { "steps" : [ { "join_preparation" : { "select#" : 1 , "steps" : [ { "expanded_query" : "/* select#1 */ select (1 + 1) AS `1+1`" } ] } } , { "join_optimization" : { "select#" : 1 , "steps" : [ ] } } , { "join_execution" : { "select#" : 1 , "steps" : [ ] } } ] }
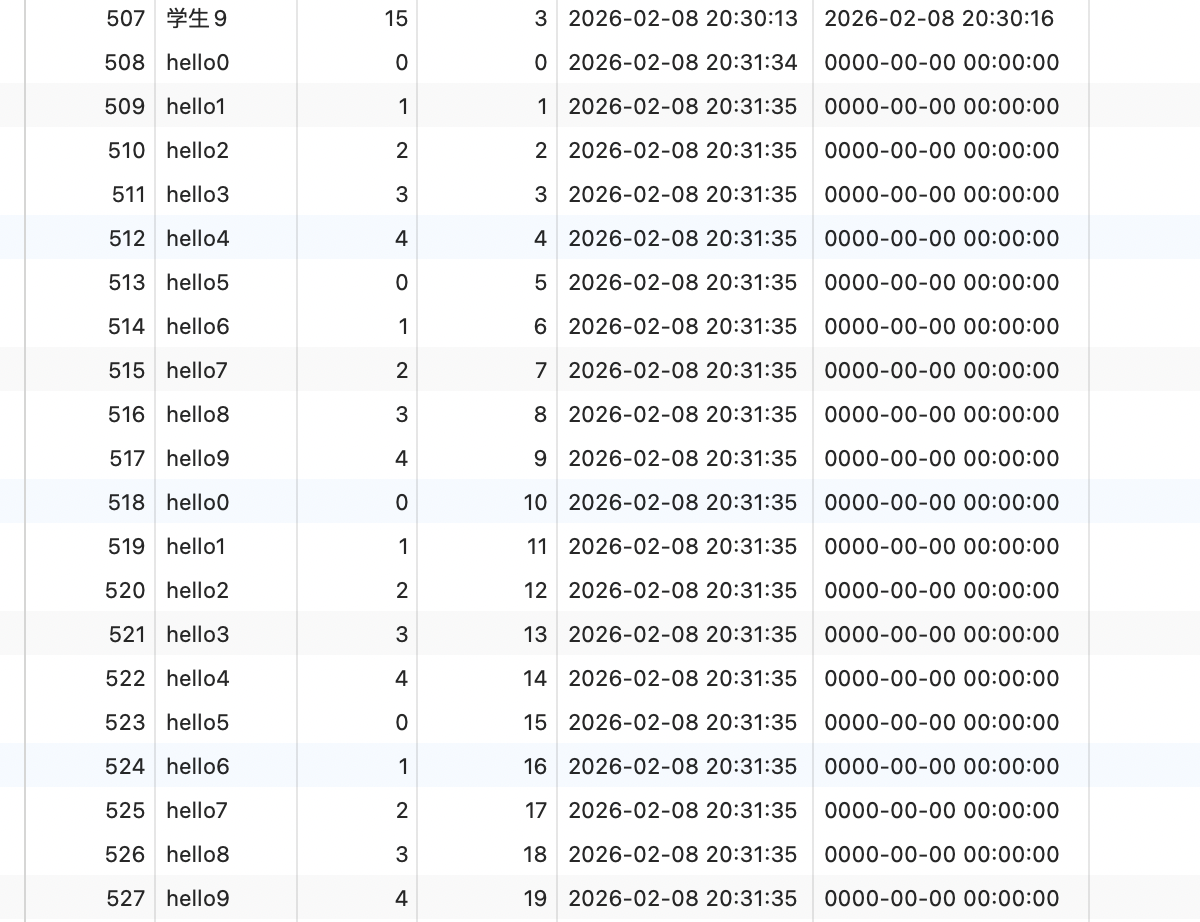
我们可以再查一个真实点的1 SELECT * from students WHERE class = 10 ;
trace 就长这样1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 159 160 161 162 163 164 165 166 167 168 169 170 171 172 173 174 175 176 177 178 179 180 181 182 183 184 185 186 187 188 189 190 191 192 193 { "steps" : [ { "join_preparation" : { "select#" : 1 , "steps" : [ { "expanded_query" : "/* select#1 */ select `students`.`id` AS `id`,`students`.`name` AS `name`,`students`.`age` AS `age`,`students`.`class` AS `class`,`students`.`created_at` AS `created_at`,`students`.`updated_at` AS `updated_at` from `students` where (`students`.`class` = 10)" } ] } } , { "join_optimization" : { "select#" : 1 , "steps" : [ { "condition_processing" : { "condition" : "WHERE" , "original_condition" : "(`students`.`class` = 10)" , "steps" : [ { "transformation" : "equality_propagation" , "resulting_condition" : "multiple equal(10, `students`.`class`)" } , { "transformation" : "constant_propagation" , "resulting_condition" : "multiple equal(10, `students`.`class`)" } , { "transformation" : "trivial_condition_removal" , "resulting_condition" : "multiple equal(10, `students`.`class`)" } ] } } , { "substitute_generated_columns" : { } } , { "table_dependencies" : [ { "table" : "`students`" , "row_may_be_null" : false , "map_bit" : 0 , "depends_on_map_bits" : [ ] } ] } , { "ref_optimizer_key_uses" : [ { "table" : "`students`" , "field" : "class" , "equals" : "10" , "null_rejecting" : false } ] } , { "rows_estimation" : [ { "table" : "`students`" , "range_analysis" : { "table_scan" : { "rows" : 107 , "cost" : 24.5 } , "potential_range_indexes" : [ { "index" : "PRIMARY" , "usable" : false , "cause" : "not_applicable" } , { "index" : "idx_class" , "usable" : true , "key_parts" : [ "class" , "id" ] } ] , "setup_range_conditions" : [ ] , "group_index_range" : { "chosen" : false , "cause" : "not_group_by_or_distinct" } , "analyzing_range_alternatives" : { "range_scan_alternatives" : [ { "index" : "idx_class" , "ranges" : [ "10 <= class <= 10" ] , "index_dives_for_eq_ranges" : true , "rowid_ordered" : true , "using_mrr" : false , "index_only" : false , "rows" : 5 , "cost" : 7.01 , "chosen" : true } ] , "analyzing_roworder_intersect" : { "usable" : false , "cause" : "too_few_roworder_scans" } } , "chosen_range_access_summary" : { "range_access_plan" : { "type" : "range_scan" , "index" : "idx_class" , "rows" : 5 , "ranges" : [ "10 <= class <= 10" ] } , "rows_for_plan" : 5 , "cost_for_plan" : 7.01 , "chosen" : true } } } ] } , { "considered_execution_plans" : [ { "plan_prefix" : [ ] , "table" : "`students`" , "best_access_path" : { "considered_access_paths" : [ { "access_type" : "ref" , "index" : "idx_class" , "rows" : 5 , "cost" : 4 , "chosen" : true } , { "access_type" : "range" , "range_details" : { "used_index" : "idx_class" } , "chosen" : false , "cause" : "heuristic_index_cheaper" } ] } , "condition_filtering_pct" : 100 , "rows_for_plan" : 5 , "cost_for_plan" : 4 , "chosen" : true } ] } , { "attaching_conditions_to_tables" : { "original_condition" : "(`students`.`class` = 10)" , "attached_conditions_computation" : [ ] , "attached_conditions_summary" : [ { "table" : "`students`" , "attached" : null } ] } } , { "refine_plan" : [ { "table" : "`students`" } ] } ] } } , { "join_execution" : { "select#" : 1 , "steps" : [ ] } } ] }
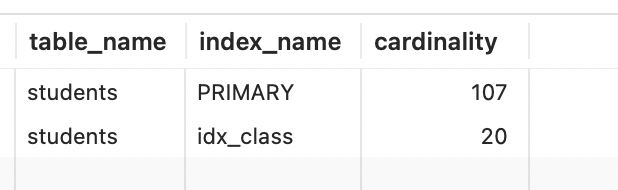
比如这里的 potential_range_indexes 提示primary主键就是不适用的,当然具体分析还需要更深入的学习。